Sanctions and Export Controls Update
Monthly Roundup – October 2025
📅 November 5, 2025
📅 November 5, 2025
Welcome to this month’s Sanctions and Export Controls Update, highlighting IFI’s take on key developments from October 2025.
The three most significant developments in October included:
The West significantly intensified pressure on Moscow in late October, most prominently by the EU adopting its 19th sanctions package and the U.S. and UK sanctioning Rosneft and Lukoil—Russia’s two largest oil companies. The U.S. and UK also imposed sweeping sanctions against hundreds of targets associated with a Cambodia-based transnational criminal organization responsible for industrial scale cyberfraud operations globally. After trade talks with China, the U.S. announced the suspension of BIS’s new 50% Affiliates Rule, which would have dramatically expanded the number of Chinese companies subject to U.S. trade restrictions.

In a major shift in the Trump administration’s sanctions policy, Treasury imposed blocking sanctions on Rosneft and Lukoil. These were the first designations targeting Russia by the second Trump administration and came after plans for a summit between Presidents Trump and Putin in Budapest fell through amidst a sustained lack of progress towards a peace deal by Russia and Ukraine. Rosneft and Lukoil produce more than 5 billion barrels of crude oil annually, which is around 50% of total Russian oil production. The U.S. sanctions were magnified the UK unleashing its strongest sanctions yet on Russia and by the EU adopting a sweeping package of new sanctions targeting Russian energy, third-country banks, and crypto providers.
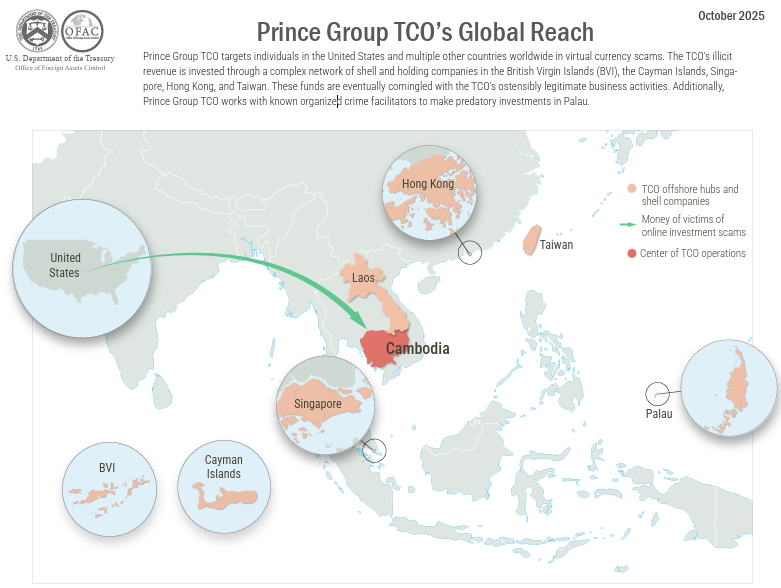
The U.S. and UK took what the Treasury Department called the largest action ever targeting cybercriminal networks in Southeast Asia. They imposed sweeping actions on over 100 targets associated the Prince Group Transnational Criminal Organization, a Phnom Penh-based network led by Cambodian national Chen Zhi. The Prince Group has reportedly carried out numerous transnational crimes including the construction, operation, and management of scam compounds reliant on human trafficking and modern-day slavery where industrial scale cyberfraud operations target victims around the world. The bilateral sanctions actions were accompanied by the unsealing of a criminal indictment in U.S. district court against Chen Zhi.
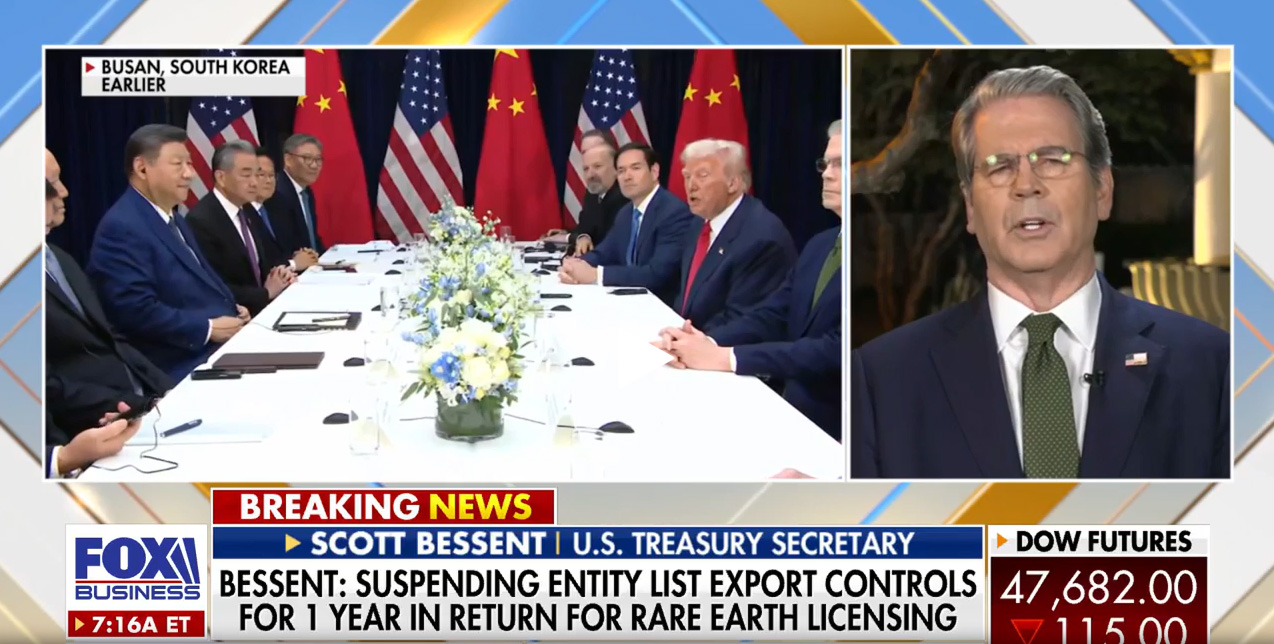
During a televised interview on 31 October, Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent announced that the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) will suspend implementation of the “Affiliates Rule” that was adopted in September. Under the rule, BIS expanded the scope of the Entity List to also apply to non-U.S. entities owned, directly or indirectly, 50% or more by another party or parties included on the Entity List. This would have dramatically expanded the number of Chinese companies subject to U.S. trade restrictions. According to Bessent, the rule would be suspended for one year in exchange for China’s suspension of its proposed export controls on rare earth minerals.
Treasury Identifies $9 Billion of Potential Iranian Shadow Banking Activity in 2024
Treasury’s FinCEN issued a 20-page report identifying approximately $9 billion of potential Iranian shadow banking activity that occurred through U.S. correspondent accounts in 2024, based on reporting from U.S. financial institutions. According to FinCEN, Tehran relies on shadow banking networks of Iran-based exchange houses and foreign front companies to evade sanctions, which are connected across continents – most prominently through the UAE, Hong Kong, and Singapore.

U.S. Imposes Sanctions on Iraqi Network Laundering Money for Iran
Treasury designated multiple Iraqi individuals and entities linked to Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps–Quds Force (IRGC-QF) involved in laundering money and aiding operations against American interests. The targets allegedly laundered tens of millions of dollars for Iran and engaged in corruption through political and commercial ties. According to Treasury, Iran continually seeks to take advantage of Iraq’s economy to evade sanctions, despite progress made by many Iraqi government and financial professionals to secure and modernize their institutions.
Treasury Announces New Sanctions on Iran’s Petroleum Shipment Facilitators
OFAC imposed new sanctions on more than 50 individuals, entities, and vessels linked to Iran’s petroleum and petrochemical exports. The move targets networks that have facilitated billions of dollars in Iranian oil and liquefied petroleum gas sales, including a China-based crude oil terminal and an independent “teapot” refinery.
Treasury Designates Military Procurement Networks
OFAC designated 21 entities and 17 individuals tied to Iranian procurement networks supporting the Ministry of Defense and Armed Forces Logistics (MODAFL), ballistic missile development, and military aircraft production. The designations follow the September 27 U.N. “snapback” sanctions on Iran. OFAC targeted networks operating in Iran, China, Hong Kong, Germany, Türkiye, Portugal, and Uruguay procuring sensitive technologies.
U.S. Supreme Court Rejects Appeal by Turkey’s Halkbank
The U.S. Supreme Court rejected an appeal by Turkey’s Halkbank, leaving the state-controlled lender to face criminal charges that it helped Iran to evade economic sanctions and launder billions of dollars through the American financial system.
UK Announces Sanctions on Iranian Banker for Financial Support to IRGC
The UK imposed sanctions on Iranian national Aliakbar Ansari for his role in financially supporting the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). The measures include an asset freeze, director disqualification, and a travel ban. The United Kingdom has now sanctioned more than 500 individuals and entities as part of its Iran sanctions program.
U.S. Designates Fentanyl Supply Network Linked to Sinaloa Cartel
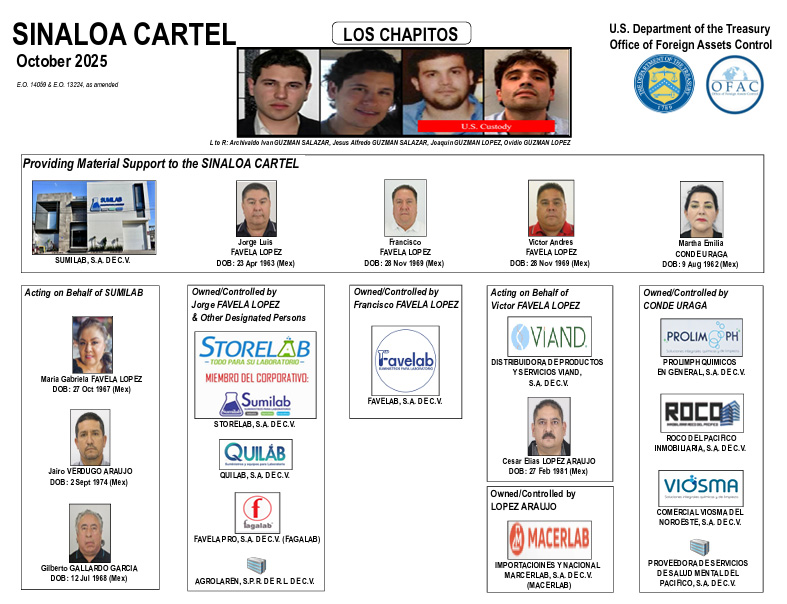
OFAC imposed sanctions on eight Mexican nationals and 12 companies tied to the Sinaloa Cartel’s Los Chapitos faction, a group led by the sons of Joaquin “El Chapo” Guzman Loera. The network allegedly supplied precursor chemicals used in illicit fentanyl production. The action targeted Culiacan-based Sumilab and related firms operated by the Favela Lopez family, which continued chemical sales to cartel-linked producers even after earlier sanctions. OFAC also sanctioned broker Martha Emilia Conde Uraga and her front companies for supplying chemicals to drug traffickers and lab operators working for the faction.
U.S. Imposes Sanctions on Mexican Human Smuggling Network
Treasury announced sanctions against the Bhardwaj Human Smuggling Organization (HSO), its leader Vikrant Bhardwaj, three associates, and 16 affiliated companies involved in human smuggling, drug trafficking, and money laundering. The group allegedly smuggled thousands of migrants from Europe, the Middle East, South America, and Asia into the U.S.
U.S. Designates Colombian President’s Support Network Over Corruption, Illicit Financing
Treasury designated three close associates of Colombian President Gustavo Petro—his son Nicolas Petro, First Lady Veronica Alcocer, and Interior Minister Armando Benedetti—for their alleged involvement in corruption and illicit financial activities supporting the president.
U.S. Sanctions Haitian Gang Leaders Tied to Terrorist Group Viv Ansanm
OFAC sanctioned former Haitian police officer Dimitri Herard and gang leader Kempes Sanon for supporting the Haitian gang coalition Viv Ansanm, designated earlier this year as a foreign terrorist organization. Herard, linked to the 2021 assassination of President Jovenel Moïse, allegedly trained and armed gang members after escaping from prison in 2024.
U.S., Japan Agree to Strengthen Critical Minerals Supply Chains

The U.S. and Japan established a new bilateral framework to strengthen cooperation on critical minerals and rare earths vital to both nations’ industries. Through coordinated investment and economic policy tools, the framework seeks to accelerate the development of diversified and transparent markets for mining, separation, and processing. It also aims to enhance resilience and security across supply chains while expanding both countries’ production capacities.
U.S. Renews Denial of Export Privileges for Ural Airlines
The U.S. Commerce Department renewed a ban on Ural Airlines’ export privileges for another year due to ongoing violations of U.S. export controls. The Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) cited repeated, deliberate breaches of the Export Administration Regulations, including unauthorized flights into and within Russia using U.S.-origin aircraft parts.
Commerce Department, Luminultra Reach Settlement Over Unauthorized Exports to Iran
According to BIS, the Canadian firm shipped three PhotonMaster luminometers and 25 aqueous test kits to Iran in 2022 without U.S. authorization. A luminometer is an instrument used to measure visible light emitted by a sample, typically produced by a chemical or biological reaction. The company allegedly disguised the shipment by listing a UAE-based entity as the consignee to conceal that Iran was the true destination. Luminultra agreed to pay a $685,051 civil penalty and conduct annual export compliance audits for three years.
Cyprus Passes Law to Tighten Foreign Investments Screening
Cyprus’ parliament approved legislation to strengthen the screening of foreign direct investment (FDI) in sectors deemed sensitive to national security. The law establishes a national mechanism to monitor foreign investments worth at least EUR 2 million (USD 2.3 million), aligning Cyprus with the European Union’s 2020 FDI Screening Regulation. It covers transactions involving vital infrastructure, including land and property designated as strategically important. The country’s finance ministry will issue temporary guidelines until a national map of critical sites is completed.
The UN Security Council has unanimously adopted Resolution 2794 (2025), renewing for one year the sanctions regime on Haiti, including travel bans, asset freezes, and an arms embargo targeting individuals and entities destabilizing the country through illicit resource trade. The resolution also extends the mandate of the Panel of Experts on Haiti for 13 months. Haiti’s representative welcomed the renewal, calling the sanctions a key tool to deter gangs and support national stability alongside the newly formed Gang Suppression Force.
EU Extends Sanctions on ISIL, Al-Qaeda Affiliates
The Council of the EU renewed autonomous restrictive measures against ISIL (Da’esh), Al-Qaeda, and their associated groups for another year, extending them until October 31, 2026. The sanctions target 15 individuals and 7 groups through asset freezes and, for individuals, travel bans to the EU. The measures, which complement UN sanctions, underscore the EU’s continued commitment to counter global terrorism and act against those financing or supporting extremist activities.
EU Renews Russia Destabilization Sanctions
The European Council extended restrictive measures against those responsible for Russia’s destabilizing actions abroad until October 9, 2026, citing continued hybrid activities, including foreign information manipulation and interference. The sanctions regime, covering 47 individuals and 15 entities, imposes asset freezes and travel bans and bars EU citizens and companies from providing funds or economic resources.
EU Extends Sanctions Against Moldova’s Transnistrian Leaders
The Council of the EU extended Decision 2010/573/CFSP, which was set to expire on October 31, by another year. The Decision imposes restrictive measures on leaders of Transnistria, a breakaway region internationally recognized as part of the Republic of Moldova. The extension follows the proposal from the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy.
EU Extends Sanctions Over Chemical Weapons Use
The Council of the EU extended by one year its restrictive measures targeting the proliferation and use of chemical weapons, keeping them in place until October 16, 2026. The sanctions, including asset freezes, funding restrictions, and EU travel bans, currently apply to 25 individuals and six entities. The sanctions framework allows for updates based on new developments, such as the May 2025 addition of three Russian entities linked to chemical weapons use in Ukraine.










 OFAC’s 50 Percent Rule
OFAC’s 50 Percent RuleThis site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
Accept settingsHide notification onlySettingsWe may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
These cookies collect information that is used either in aggregate form to help us understand how our website is being used or how effective our marketing campaigns are, or to help us customize our website and application for you in order to enhance your experience.
If you do not want that we track your visit to our site you can disable tracking in your browser here:
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
Privacy Policy